Digestive system is uniquely constructed to perform its specialized function of turning food we eat into nutrients, which the body then uses for energy we need to survive, growth, cell repair and packaging the waste to be eliminated. The food that we eat, undergoes 6 major processes:
- Swallowing – voluntary.
- Peristalsis – involuntary, involves alternating contractions of muscles in body walls of GI organs.
- Prepares food for chemical digestion.
- Includes chewing, mixing with saliva by tongue action, churning in stomach, etc.
- Catabolic steps in which food is broken down to basic building blocks.
- Accomplished by enzymes in digestive juices.
There are 2 parts of human digestive system: Main Parts and Accessory Parts 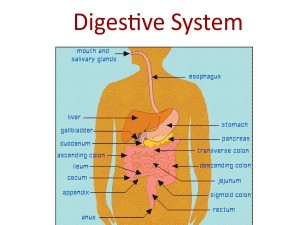
Main Parts:
- Mouth
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small Intestine
- Large Intestine
- Rectum
- Anus
Accessory Parts:
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Gallbladder
- Salivary Gland
The process of digestion starts from the mouth and ends at the anus.
Main Parts
Mouth: Physical and chemical digestion occurs
Esophagus: A long soft tube that runs from the mouth to the stomach. It uses rhythmic muscle movements (called peristalsis) to force food from the throat into the stomach.
Stomach: Sack-like, muscular organ that is attached to the esophagus, where both chemical and mechanical digestion takes place. It is where digestion of protein begins and has three tasks: stores swallowed food; mixes the food with stomach acids; and sends the mixture on to the small intestine. When food enters the stomach, it is churned in a bath of acids (Hydrochloric Acid) and enzymes. Partly digested food mixed with stomach acid is called Chyme.
Small Intestine (3 parts and 6 Meters Long): Chemical digestion and the absorption of nutrients into the blood. Once digested in the stomach, food enters the first part of the small intestine called the duodenum, then to the jejunum and finally into the last part of the small intestine the ileum. In the small intestine, bile (produced in the liver and stored in the gall bladder), pancreatic enzymes and other digestive enzymes produced by the inner wall of the small intestine further assist with the breakdown of food.
Large intestine: Absorption of water from the food remains. From the small intestine, food enters the large intestine, where some of the water and electrolytes (chemicals like sodium) are removed from the food.
Rectum: Solid waste is then stored in the rectum until it is excreted via the anus.
Anus: Where solid waste is excreted.
Accessory Parts
Pancreas: Enzyme-producing gland located below the stomach and above the intestines. Enzymes from the pancreas help in the digestion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the small intestine.
Liver: Largest organ in the Digestive System which is located above and in front of the stomach. It filters toxins from the blood, and makes bile (which breaks down fats) and some blood proteins.
Gallbladder: Small, sac-like organ located by the duodenum. It stores and releases bile (a digestive chemical which is produced in the liver) into the small intestine.
Salivary Gland: Located in the mouth producing saliva. Saliva contains enzymes called Salivary Amylase that help break down carbohydrates (starch) into smaller molecules.
GUT (Digestive Tract)
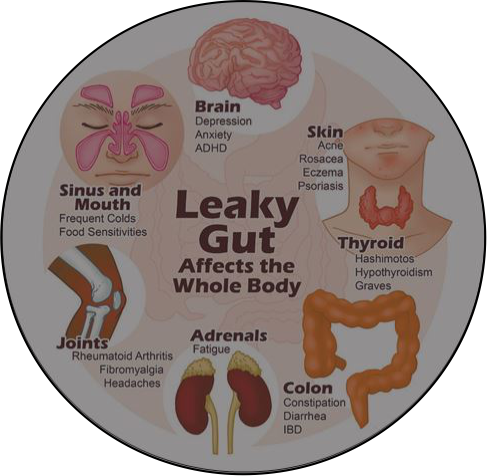
The gut plays a vital role in maintaining the overall health of the body. It refers to the entire digestive tract of the body. It’s responsibe for the absorption of nutrients and prevent the toxins from being absorbed in your blood stream. A healthy gut provides the necessary nutrition for the body and ensures the elimination of toxins from your body and not ending up affecting your health. The gut also keeps everything moving through it properly.
In fact, an upset stomach is often one of the first symptoms of a health issue in your body. Unlike in other parts of the body, any issue with the gut is immediately noticeable. Gut issues can be either temporary or chronic. Anything ingested can affect your body through the stomach and the intestines. Thus, if your digestive system is inefficient, your health is bound to suffer because the gut contributes to the overall physiological and physical health. And it’s also possible for the digestive Issuess to affect the entire body, contributing to numerous health complications, such as: Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Allergies, Skin Diseases, Liver Disease, Immunity Diseases, Cancer, Arthritis, Depression, etc.
The gut acts as a shield for the immune system, and when it’s inflammed, it can lead to food intolerances, which can lead to immune system problems. You can also develop autoimmune diseases (whereby your immune system becomes confused and begins to attack your own body). When it’s affected, you become more vulnerable to a variety of sicknesses. Dietary imbalances, medications or even stress can affect the balance of the bacteria present in the digestive tract. This increases your susceptibility to various health conditions.
Liver & Pancreas Detox
(Liver Detox for Liver-Related Diseases & Pancreas Detox for Diabetes)
Complementory Therapy
- Liver Detox
- Yoga Therapy
Liver & Pancreas Detox
- Patient to lie flat with legs folded during stimulation. Place a bolster under knees.
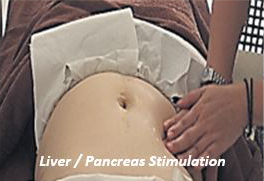 Use herbal oil for stimulation of the liver / pancreas which is located at the upper right quadrant of the abdominal cavity.
Use herbal oil for stimulation of the liver / pancreas which is located at the upper right quadrant of the abdominal cavity.- Stimulation is applied while exhaling using one hand on top of the other at the liver / pancreas region. Alternate with gentle rotation and repeat for about 20 minutes.
- Stimulate 3 to 5 rounds on the abdomen, starting from the Caecum (on right side of stomach) to Sigmoid colon for about 10 minutes.
- Thereafter, use hot pad after the stimulation (for 10 minutes); followed by cold pad (10 minutes).
- Rest in Quick Relaxation Technique (QRT).
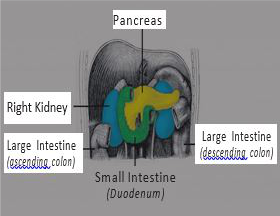 ** Liver performs various functions. One of the most important is Detoxification. It detoxifies harmful substances in two steps. The first step uses enzymes and oxygen to burn toxins, especially fatty ones, so they are more water soluble, making them easier for the body to eliminate. The second step combines partially processed toxins with sulfur or amino acids so they can be removed through bile or urine.
** Liver performs various functions. One of the most important is Detoxification. It detoxifies harmful substances in two steps. The first step uses enzymes and oxygen to burn toxins, especially fatty ones, so they are more water soluble, making them easier for the body to eliminate. The second step combines partially processed toxins with sulfur or amino acids so they can be removed through bile or urine.By performing the above mentioned detox (stimulation with deep relaxation), the movements performed stimulates the organs which in turn improves metabolic activities. The chemical transformations within a cell are carried out more efficiently making it a highly beneficial exercise for those suffering from liver-related diseases and diabetes.
** In the process of detoxin, these toxins are being eliminated from the body via:
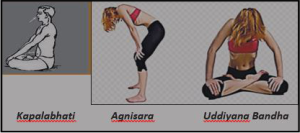 Yoga Therapy
Yoga Therapy
a. Pranayama & Bandhas
- Kapalabhati (20 breaths x 5)
- Agnisara (9 breaths x 5 )
- Uddiyana Bandha ( 9 breath x 5
- Moola Bandha : contraction of the perineum
- Uddiyana Bandha : contraction of the abdomen into the rib cage
- Jalandhara Bandha : tucking the chin close to the chest
- Maha Bandha : combining all three of the above bandhas
Benefits
As the Bandhas momentarily stop the flow of blood, there is an increased flow of fresh blood with the release of the Bandha, which flushes away old, dead cells. In this way all the organs are strengthened, renewed and rejuvenated and circulation is improved.
Bandhas are also beneficial for the brain centres, the Nadis and the Chakras. The energy channels are purified, blockages released and the exchange of energy is improved. Bandhas alleviate stress and mental restlessness and bring about inner harmony and balance.
b. Tiger breathing (9 rounds)
Starting pose: Vajrasana
- Lean forward, press the palms on the ground and stand on your knees. Arms, thighs and heels should be shoulder width apart. Shoulder and wrist in one straight line
 While inhaling, raise the head and look at the ceiling. Depress the spine, making it concave
While inhaling, raise the head and look at the ceiling. Depress the spine, making it concave- While exhaling, round your shoulders, suck in your belly and bring the chin towards the chest
c. All deep twisting yoga poses (5 rounds)
All practices repeated slowly with awareness and pressure to abdomen for stimulation
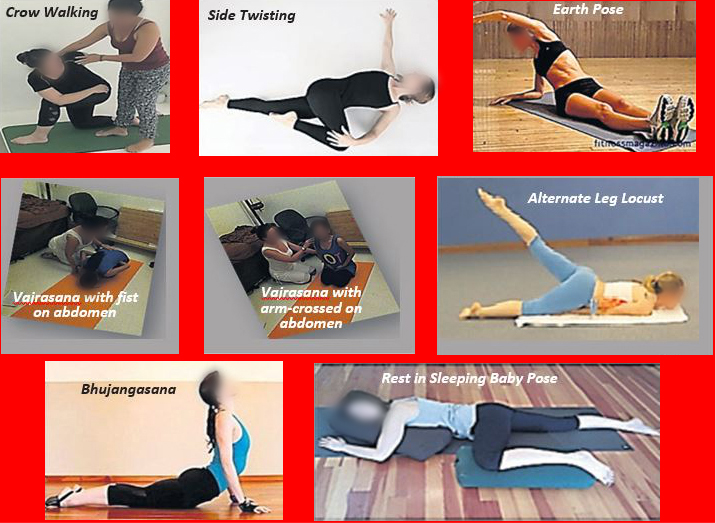
- Crow walking (twist walk up and down)** Right and left twist, hands in opposite direction
- Side twisting
- Earth pose** Sit in dandasana and twist to the back placing arms on the ground
- Vajrasana with fist on abdomen and forward fold
- Vajrasana with arm crossed on abdomen & forward fold
- Alternate leg Locust with fist at abdomen** Lie down on your chest with forehead on the floor ; make a fist with your hands and place it at the abdomen. Lift one leg off the mat.
- Bhujangasana twisting –inhale up , exhale twist and look back** Rest in sleeping baby pose without pillow (Alternate right & left)
d. Quick Relaxation Technique (QRT) in Savasana (Corpse Pose)
e. MSRT / PET / CM or DRT
MSRT – Mind Sound Resonance Technique
It’s a powerful technique which uses sound vibrations (spoken – Ahata and unspoken – Anahata). It’s one of the mindfulness based relaxation techniques in which resonance is generated by chanting the mantras which revitalizes the internal energy. It leads to deep relaxation of the mind and body. Practice of MSRT enhances the relaxation, well-being, will power, improved cognitive performance, etc. It harnesses the power of positive resolve to bring about beneficial changes.
PET – Pranic Energisation Technique
A technique in which we use our Prana Shakthi to energise our entire body. It strengthened the immune defense so that modern dreaded killer diseases can be effectively healed. This technique also cleanses the respiratory tract, normalizing the functions of respiratory systems purifying the subtle channels of PRANA, bringing the balance in PRANAMAYA KOSHA and gaining deeper and subtler insights for the control of Prana. Each and every organs and systems of the body gets revitalized and energized by this process and brings harmony in the body and mind. All ailments can be eliminated from body and the rootcause from mind is also eliminated.
Cyclic Meditation (CM)
It’s a meditation technique named as moving meditation taken from Mandukya Upanishad. It’s a guided meditation with a combination of alternate stimulation followed by relaxation techniques. Stimulation is done by stretching part by part; and relaxation by three relaxation techniques which are Instant Relaxation Technique (IRT) , Quick RelaxationTechnique (QRT) and Deep RelaxationTechnique (DRT). An essential part of the practice of CM is being aware of sensations arising in the body.
Subtle Point
- For patient with acute /chronic back pain – avoid deep twisting
Indication
- Poor digestion
- Recurrent diarrhea
- IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
- Gastric , colic pain
- High Cholesterol
Contraindication
- Liver Surgery
- Liver Cancer
- Liver failure
- Peptic Ulcer
- Surgery at the abdominal area
Acknowledgement to:
- CYT / ATTC Students of Union Yoga Ayurveda Singapore
- Swami Vivekananda Yoga Prakashana Trust, Bangalore
Disclaimer
Yoga Ayurveda Therapy is Complementary Medicine and doesn't alternates any conventional treatment.
Yoga-Ayurveda Therapy needs physical assistance which may need physical touch. You can ask teacher or therapist not to give physical touch or assistance and based on whatever you choose, our teacher or therapist will follow the instructions. Any point you want to change the preference, then please inform teacher or therapist and management in writing. You will take responsibility of your decision and will not hold Union Yoga Ayurveda responsible for any kind of damage.
All kind of Yoga Ayurveda teaching and therapy can cause certain injuries and you are accepting those injuries. Signing up for the therapy or yoga courses means that you are aware of the probable injuries.
Union Yoga Ayurveda (Union Centre Pte Ltd) and its staff are not liable or responsible for any injuries caused during the session which are visible or not visible, physical or hormonal or mental. You as client take full responsibility of your own decision and will not claim any kind of compensation in terms of money or any resources for the damage caused because of due process.
Related Topics
- Yoga Therapy & Common Ailments
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Yoga & Glaucoma
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Gastro-Esophageal Reflux / Gastritis
- High Blood Pressure
- For Anxiety neurosis, Depressions etc
- For Neurological issues
- Cataract and short / long Sightedness
- Scoliosis / Herneated disc / Sciatica
- Menstrual Issues