Uterus
Also known as the womb, is a hollow pear-sized organ which is part of the reproductive structure of the female anatomy, located in a woman’s lower abdomen, between the bladder and the rectum. Although the Uterus is quite small in size, it’s responsible for the most important aspect of human life: continuity of the human species. The cervix is the lower portion of the uterus. It contains the cervical canal, which has a narrow openings towards the uterus and the vagina called the os.
The cervical canal connects the uterine cavity to the vagina and allows menstrual blood to flow out of the uterus into the vagina. The fallopian tubes connect the uterus and ovaries. Ovaries are egg-producing organs that hold 200,000 to 400,000 follicles which contain the materials needed to produce ripened eggs, or ova. An egg develops within the follicle.
Uterus is made up of three layers of tissue:
The Endometrium: Inside layer of the uterus that is the layer that builds up over the course of a month and is shed each month if no pregnancy occurs. This shedding of the lining of the uterus is the menstrual period. When pregnancy occurs, the endometrium supplies nutrients to the fertilized egg, and eventually supports the placenta. The muscular nature of the uterus allows it to expand to accommodate a growing fetus. During childbirth muscular contractions in the uterus help to push the baby out of the body.
 Menstruation
Menstruation
It’s the periodical flow of blood from the uterus through the cervix and out through the vagina, and commonly known as “period”. Menstrual flow consists of blood and mucus from the cervix and vagina. It occurs during the years between puberty and menopause and are a normal part of a woman’s life. Menstruation is essential for the renewal of the uterine lining in preparation for pregnancy. The process of degeneration of endometrial bed and removal of the same through vagina occurs at regular interval and is called the menstrual cycle.
The menstrual cycle is regulated by the complex surge and fluctuations in many different reproductive hormones. These hormones work together to keep healthy as well as prepare a woman’s body for pregnancyeach month. The hypothalamus (an area in the brain) and the pituitary gland control six important hormones:
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is released by the hypothalamus. GnRH stimulates the pituitary gland to produce Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH). Female hormones Estrogen and Progesterone, and the male hormone Testosterone are secreted by the ovaries at the command of FSH and LH.
Menstrual Issuess
There are several types of menstrual Issuess. Problems ranging from heavy, painful periods to no periods at all. Many different factors can trigger menstrual Issuess, including hormone imbalances, genetic factors, clotting Issuess and pelvic diseases. There are many variations in menstrual patterns, but in general women should be concerned when periods come fewer than 21 days or more than 3 months apart, or if they last more than 10 days. Such events may indicate ovulation problems or other medical conditions. Some of the more common Issuess experienced are:
Dysmenorrhea (Painful Cramps) Severe, frequent cramping during menstruation. Pain occurs in the lower abdomen but can spread to the lower back and thighs. It’s usually referred to as primary or secondary:
- Primary dysmenorrhea > Cramping pain caused by menstruation, which occurs from contractions in the uterus and are usually more severe during heavy bleeding
- Secondary dysmenorrhea > Menstrual-related pain that accompanies another medical or physical condition, such as endometriosis or uterine fibroids.
Menorrhagia (Heavy Bleeding) Menorrhagia is the medical term for significantly heavier / abnormal periods. Menorrhagia can be caused by a number of factors. During a normal menstrual cycle, the average woman loses about 1 ounce (30 mL) of blood, changing her tampons or pads around 3 to 6 times per day because flow lasts longer and is heavier than normal. The bleeding occurs at regular intervals (during periods) and usually lasts more than 7 days and women lose an excessive amount of blood. Clot formation is common. Menorrhagia is often accompanied by dysmenorrhea because passing large clots can cause painful cramping
Other types of abnormal bleeding are:
- Metrorrhagia > Also called breakthrough bleeding, refers to bleeding that occurs at irregular intervals and with variable amounts. The bleeding occurs between periods or is unrelated to periods. Spotting or light bleeding between periods is common in girls just starting menstruation and sometimes during ovulation in young adult women.
- Menometrorrhagia > Refers to heavy and prolonged bleeding that occurs at irregular intervals.
- Menemetrorrhagia > Combines features of menorrhagia and metrorrhagia. The bleeding can occur at the time of menstruation (like menorrhagia) or in between periods (like metrorrhagia).
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) > A general term for abnormal uterine bleeding that usually refers to extra or excessive bleeding caused by hormonal problems, usually lack of ovulation (anovulation). Tend to occur either when girls begin to menstruate or when women approach menopause, but it can occur at any time during a woman’s reproductive life.
Complementory Therapy
- Peristalsis
- Yoga Therapy

Peristalsis
Using Gandharva Hastadi Thaila & Mustard Oil
Peristalsis is a series of contractions that pushes solids or liquids through tubes in certain parts of the body, primarily the digestive system. Basically, it’s a wave of contractions, such as those used by the esophagus and small intestines to move food through the system. In the case of menstrual Issues, Uterine peristalsis creates rhythmic spontaneous contractions of the muscular wall of the uterus, stimulation with deep relaxation.
Some of the functions of uterine peristalsis include: removal of menstrual debris; rapid transportation of sperm for fertilzation in the fallopian tube; transportation of embryo to a proper implantation site.
Procedure
- Pour a teaspoon of each type of oil (Mustard & Herbal Oil as prescribed by Doctor) into a glass bowl and place it on a warmer or heat it in microwave for 30 seconds
- Pour the warm oil slowly into the naval and let it slowly absorb through the naval into the reproduction organ
- With the remaining oil, use Peristalsis movement to stimulate the absorption of the oil into the organ
- Synchronise peristalsis movement with slow deep breathing through the nostrils for 20 minutes
- Place hot pad on lower abdomen for 20 minutes; followed by cold pad thereafter for 10 minutes
- Allow patient to rest with Quick Relaxation Technique (QRT) for 7 – 10 minutes
Yoga Therapy
a. Preparatory Practices (5 rounds each)


- Ardha Chakrasana to Padahastana – Backward and forward bending* Gradual movement from back to front, breath centeredChanting M-Kara at exhalation
- Squat – Hip Opening
- Crow Walking
- Cat Walking



b. Quick Relaxation Technique (QRT)
c. Main Practices (5 rounds each)
All practices repeated slowly with awareness and pressure to abdomen for stimulation

- Vajrasana with fist on abdomen & forward fold
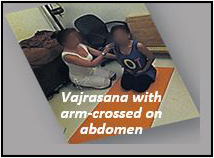
- Vajrasana with arm crossed on abdomen & forward fold
- Alternate leg locust with fist at abdomenPlace the top of one feet pressing into the floor, forehead on the floor and hands underneath your shoulders with fist at the abdomen. Lift one leg off the mat.

- BhujangasanaBreathe normally and maintain the final position for about 1 minute.
- Rest in sleeping baby pose without pillow (Alternate right & left)
- Earth pose (twist to the back placing arms on the ground)



d. Pranayama & Bandhas
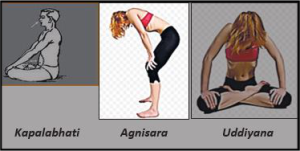
- Kapalabhati (20 breath x 5)
- Agnisara (9 breath x 5)
- Uddiyana Bandha (9 breath x 5)
Subtle Point
- Focus on abdominal region especially ovary and uterus.
- Patient with chronic surgery at abdominal area; avoid during menstrual period.
Indication
- Menstrual Issues – Fibroids , blood clotting , polyps.
- Dysmenorrhea –difficult and painful menstruation; heavy bleeding or heavy period.
Contraindication
- Recent surgery and tumour in abdominal area during menstruation.
Acknowledgement to:
- CYT / ATTC Students of Union Yoga Ayurveda Singapore
- Swami Vivekananda Yoga Prakashana Trust, Bangalore
Disclaimer
Yoga Ayurveda Therapy is Complementary Medicine and doesn't alternates any conventional treatment.
Yoga-Ayurveda Therapy needs physical assistance which may need physical touch. You can ask teacher or therapist not to give physical touch or assistance and based on whatever you choose, our teacher or therapist will follow the instructions. Any point you want to change the preference, then please inform teacher or therapist and management in writing. You will take responsibility of your decision and will not hold Union Yoga Ayurveda responsible for any kind of damage.
All kind of Yoga Ayurveda teaching and therapy can cause certain injuries and you are accepting those injuries. Signing up for the therapy or yoga courses means that you are aware of the probable injuries.
Union Yoga Ayurveda (Union Centre Pte Ltd) and its staff are not liable or responsible for any injuries caused during the session which are visible or not visible, physical or hormonal or mental. You as client take full responsibility of your own decision and will not claim any kind of compensation in terms of money or any resources for the damage caused because of due process.
Acknowledgement to:
- Yoga Therapy & Common Ailments
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Yoga & Glaucoma
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Gastro-Esophageal Reflux / Gastritis
- High Blood Pressure
- For Anxiety neurosis, Depressions etc
- For Neurological issues
- Cataract and short / long Sightedness
- Scoliosis / Herneated disc / Sciatica
- Menstrual Issues