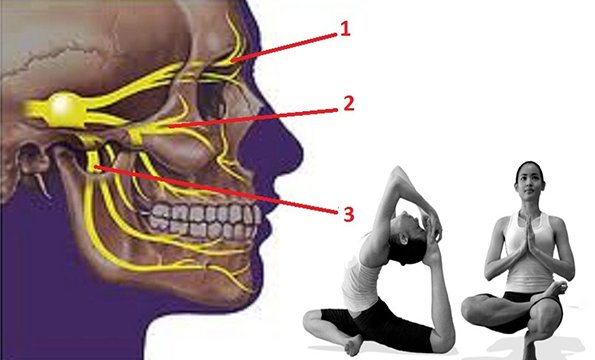
What is Trigeminal Neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia, also called tic douloureux, is a condition that affects the trigeminal nerve (the 5th cranial nerve), one of the largest nerves in the head. The trigeminal nerve is responsible for sending impulses of touch, pain, pressure, and temperature to the brain from the face, jaw, gums, forehead, and around the eyes. Trigeminal neuralgia is characterized by a sudden, severe, electric shock-like or stabbing pain typically felt on one side of the jaw or cheek. The Issues is more common in women than in men and rarely affects anyone younger than 50. The attacks of pain, which generally last several seconds and may be repeated one after the other, may be triggered by talking, brushing teeth, touching the face, chewing, or swallowing. The attacks may come and go throughout the day and last for days, weeks, or months at a time, and then disappear for months or years.
Is there any complementary Management in modern medicine?
complementary Management for trigeminal neuralgia typically includes anticonvulsant medications such as carbamazepine or phenytoin. Baclofen, clonazepam, gabapentin, and valproic acid may also be effective and may be used in combination to achieve pain relief. If medication fails to relieve pain, surgical complementary Management may be recommended.
Can Yoga reduces the pain?
According to yoga pain is a physical (annamaya kosa) manifestation of excessive speed of the prana. The uncontrolled excess of prana leads to construction and blockage of prana nadis (channels). In the system of acupuncture this is described as blockage of meridians through which the Chi(or QI) flows. These are two hints in yoga that helps you to manage your pain 1. Lean to feel the excessive activity in the area of pain. Pain is an experience of too many sensory nerves being triggered. 2.The trick to reduce pain is through slowing down this speed.
How to reduce this speed?
Through deep slow breathing. Breathing is a wonderful tool to reduce the speed of the mind and body. Focus you mind on the area of pain as you breath in defocus or slowdown and expand your awareness from this point of pain as you breath out. You can start off with fast breathing and then go reducing the rate of breathing. Start with 20 strokes of Kapalabhati, as you focus on the area of pain. Then breath slowly and expand your awareness. repeat 10 minits of practice of this alternate fast and slow breathing at least 5 times in a day.
The list other practices to be use in the management of Trigeminal Neurosis includes 1. Jogging 2. Ardhakati Cakrasana 3. Ardha Cakrasana, 4. Trikonasana 5. Neck movements – forward backward bending, right and left bending, clockwise and anticlockwise bending. 6. Bhujangasana, Shalabhasana 7. MSRT in Shavasana 8. Kapalabhati 9. Nadisuddhi – 9 rounds 10. Seetali/ Sithkari – 9 roundsParsva Sirsasana l
l
Parsva means side or flank. In this variation of Sirsasana, the trunk and legs are turned sideways on either side while balancing without disturbing the position of the head or hands.
Technique1. From the straight Salamba Sirsasana, exhale and mover the spine with a twist to the right; except the head and the hands turn the body sideways. 2. The legs and navel should face sideways 90 degrees to their originals positions as in the illustrations. One should feel the stretch near the region of the floating ribs. 3. Hold the pose from 20 to 30 seconds with normal breathing. 4. Exhale, come back to the straight Salamba Sirsasana. Take a breath, exhale and repeat the pose on the left side for the same length of time exhale and come to the straight position of Salamba Sirsasana.
Disclaimer
Yoga Ayurveda Therapy is Complementary Medicine and doesn't alternates any conventional treatment.
Yoga-Ayurveda Therapy needs physical assistance which may need physical touch. You can ask teacher or therapist not to give physical touch or assistance and based on whatever you choose, our teacher or therapist will follow the instructions. Any point you want to change the preference, then please inform teacher or therapist and management in writing. You will take responsibility of your decision and will not hold Union Yoga Ayurveda responsible for any kind of damage.
All kind of Yoga Ayurveda teaching and therapy can cause certain injuries and you are accepting those injuries. Signing up for the therapy or yoga courses means that you are aware of the probable injuries.
Union Yoga Ayurveda (Union Centre Pte Ltd) and its staff are not liable or responsible for any injuries caused during the session which are visible or not visible, physical or hormonal or mental. You as client take full responsibility of your own decision and will not claim any kind of compensation in terms of money or any resources for the damage caused because of due process.