Bladder
The urinary bladder is a muscular sac, acting as a storage organ located in the pelvic cavity anterior to the rectum and superior to the reproductive organs of the pelvis. When empty, the bladder is about the size and shape of a pear. In females the urinary bladder reduced in size it has to share the limited space of the pelvic cavity with the uterus that rests superior and posterior to it. During pregnancy the uterus takes up more space, and thus limiting the expansion of the urinary bladder.
The urinary bladder is made of 3 tissue layers that stretch to accommodate urine:
- Mucosa layer: The innermost layer of the bladder that lines the hollow lumen
- Submucosa layer: Surrounding the mucosal layer and are connective tissue with blood vessels and nervous tissue that supports and controls the surrounding tissue layers
- Muscularis layer: The visceral muscles of the muscularis layer surround the submucosa and provide the urinary bladder with its ability to expand and contract. It’s commonly referred to as the detrusor muscle and contracts during urination to expel urine from the body. It also forms the internal urethral sphincter, a ring of muscle that surrounds the urethral opening and holds urine in the urinary bladder. During urination, the sphincter relaxes to allow urine to flow into the urethra.
Urine is made in the kidneys and travels down two tubes called Ureters to the bladder. During urination, the bladder muscles contract, and two sphincters (valves) open to allow urine to flow out. Urine exits the bladder into the Urethra, which carries urine out of the body. Urine is stored in the bladder until you are ready to empty it.
When you go to the toilet your bladder outlet muscles (urethral sphincter and pelvic floor) relax and your bladder contracts (squeezes) emptying your bladder of urine. Your brain controls your bladder by sending messages to tell it when to hold on and when to empty.
People who experience accidental or involuntary loss of urine from the bladder may be suffering from Urinary Incontinence.
Urinary Incontinence
It’s the loss of bladder control which is a common and often embarrassing problem. The severity ranges from occasionally leaking urine when coughing or sneezing, to having a sudden and strong urge to urinate that you don’t get to a toilet in time.
Though it occurs more often in older people, urinary incontinence isn’t an inevitable consequence of aging and it can affect your daily activities. Types of urinary incontinence include:
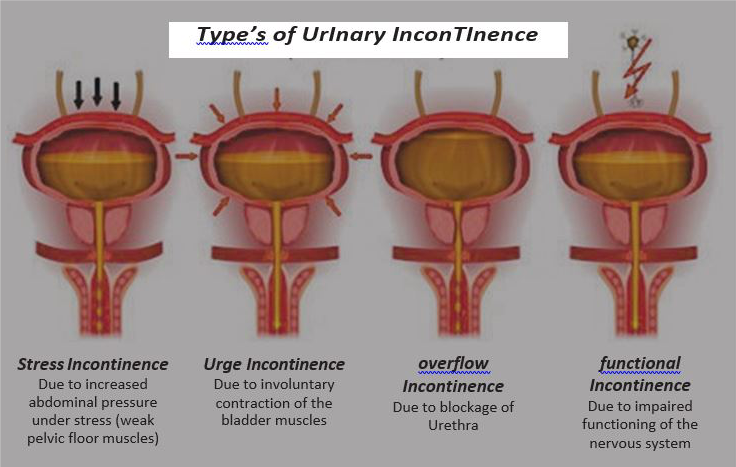
Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence occurs when the muscles and other tissues that support the bladder (pelvic floor muscles) and the muscles that regulate the release of urine (urinary sphincter) weaken. When those muscles weaken, anything that exerts force on the abdominal and pelvic muscles such as sneezing, bending over, lifting, or laughing hard can put pressure on your bladder and cause urine leakage. The pelvic floor muscles and urinary sphincter may lose strength because of:
- Childbirth: in women, poor function of pelvic floor muscles or the sphincter may occur because of tissue or nerve damage during delivery of a child. Stress incontinence from this damage may begin soon after delivery or occur years later.
- Prostate surgery: in men, the most common factor leading to stress incontinence is the surgical removal of the prostate gland (prostatectomy) to treat prostate cancer. Because the sphincter lies directly below the prostate gland and encircles the urethra, a prostatectomy may result in a weakened sphincter.
Urge Incontinence
Also known as overactive bladder or spastic bladder, it’s an involuntary loss of urine that usually occurs when a person has a strong, sudden need to urinate. Urge incontinence is not a disease. It’s caused by abnormal bladder contractions. Normally, strong muscles called sphincters control the flow of urine from the bladder but with urge incontinence, the muscles of an overactive bladder contract with enough force to override the sphincter muscles of the urethra. The bladder may experience abnormal contractions because its nerves are damaged by various diseases, for eg. diabetes, stroke, multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease; spinal cord may be damaged or the bladder may be irritated.
Overflow Incontinence
It’s the inability to control urination and occurs when you are unable to completely empty your bladder; leading to overflow, which leaks out unexpectedly. You may or may not sense that your bladder is full. The leakage, which can cause embarrassment and discomfort, is not the only problem as the urine left in the bladder is a breeding ground for bacteria which can lead to repeated urinary tract infections. Overflow incontinence is more common in men than women. The most common cause in men is an enlarged prostate, which impedes the flow of urine out of the bladder.
Functional Incontinence
A physical or mental impairment that keeps you from making it to the toilet in time, including people with musculoskeletal problems such as back pain or arthritis, or neurological problems such as Parkinson’s Issuesor multiple sclerosis (MS). In other cases, functional incontinence may result from problems with thinking or communicating. A person with Alzheimer’s Issuesor other forms of dementia, may not think clearly enough to plan trips to the restroom, recognize the need to use the restroom, or find the restroom. People with severe depression may also lose all desire to care for themselves, including using the restroom.
Complementory Therapy
Yoga therapy
Emphasise on awareness: Moola Bandha / AsWini Mudra through all postures
Steps: a – d (5 rounds each)
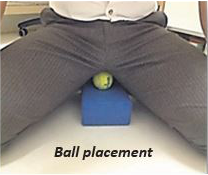
Place the tennis ball on the block and make patient sit on them. Place the tennis ball between urinary passage and anal canal for men and under vagina for women.
- a. Tiger Breathing
- b. Dog Breathing
- c. Vajrasana (Thunderbolt Pose)
- d. Ardhakati Cakrasana (Half Wheel Pose done in sitting position)
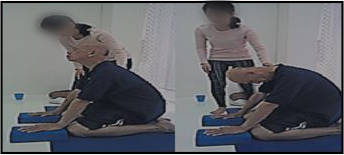


Steps: a – g (without the ball) – 5 rounds each
 Bring all the awareness to vagina area or between urinary passage and anal canal
Bring all the awareness to vagina area or between urinary passage and anal canal
- Inhale: Contract the anus, squeeze the ball
- Exhale: Relax anus and release the tension
- a. Tiger Breathing
- b. Dog Breathing
- c. Vajrasana (Thunderbolt Pose)
- d. Ardhakati Cakrasana (Half Wheel Pose done in sitting position)
- e. Ardhakati Cakrasana (Half Wheel Pose)
- f. Salabhasana (Locust Pose)
- g. Setu Bandhasana (Bridge pose)


Subtle Point
- For patient with acute / chronic back pain – avoid deep twisting
- Standby diapers
- Do not sit on ball – feel the ball to stimulate the prostate gland
Indication
- Urinary incontinence
- Infertility
- Problem with sperm count
Contraindication
- Avoid during urinary infection
- Avoid when there’s bleeding in urinary track
- Patient with abdominal surgery
Acknowledgement to:
- CYT / ATTC Students of Union Yoga Ayurveda Singapore
- Swami Vivekananda Yoga Prakashana Trust, Bangalore
Disclaimer
Yoga Ayurveda Therapy is Complementary Medicine and doesn't alternates any conventional treatment.
Yoga-Ayurveda Therapy needs physical assistance which may need physical touch. You can ask teacher or therapist not to give physical touch or assistance and based on whatever you choose, our teacher or therapist will follow the instructions. Any point you want to change the preference, then please inform teacher or therapist and management in writing. You will take responsibility of your decision and will not hold Union Yoga Ayurveda responsible for any kind of damage.
All kind of Yoga Ayurveda teaching and therapy can cause certain injuries and you are accepting those injuries. Signing up for the therapy or yoga courses means that you are aware of the probable injuries.
Union Yoga Ayurveda (Union Centre Pte Ltd) and its staff are not liable or responsible for any injuries caused during the session which are visible or not visible, physical or hormonal or mental. You as client take full responsibility of your own decision and will not claim any kind of compensation in terms of money or any resources for the damage caused because of due process.
Related Topics
- Yoga Therapy & Common Ailments
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Yoga & Glaucoma
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Gastro-Esophageal Reflux / Gastritis
- High Blood Pressure
- For Anxiety neurosis, Depressions etc
- For Neurological issues
- Cataract and short / long Sightedness
- Scoliosis / Herneated disc / Sciatica
- Menstrual Issues